Hair loss causes in women-symptoms-treatments-prevention
Losing hair is frightening. Going grey is like having an advert on your head saying: “I’m getting old!”
Let’s face it, noticeable hair loss can be deeply concerning. There are many reasons women develop thinning hair. Currently, there are more options to enhance hair growth than ever before. I don’t know about you, but many of my friends, including myself, that have noticed a significant loss in hair over the last few years.
Although the condition is more widespread among the male population, hair loss is frequently attributed to the females. You might suffer from hair loss in different areas of your body, such as thinning, widening and patchy hair loss.
This blog post focuses on hair thinning for women. Discover the underlying causes, effective treatments, and empowering solutions for female hair loss. From hormonal imbalances to lifestyle factors, we delve into the science behind hair loss and share actionable tips to promote regrowth and boost confidence. Unlock the secrets to maintaining healthy and vibrant hair for women of all ages.”

Understanding Hair Loss in Women: Causes, Treatments, and Promoting Hair Growth
Hair loss is a common concern that affects both men and women. While it is often associated with men, hair loss in women is a prevalent issue that can cause distress and impact self-esteem. When women have noticeable hair loss, it is devastating and can affect self esteem.
In this blog post, we will delve into the topic of hair loss in women, exploring its various forms, causes, and available treatment options. We will also discuss the importance of maintaining healthy hair follicles and offer tips for growing more hair.
Female Hair Loss
We are all familiar with the topic of male pattern baldness, but women rarely talk about their own issue with sudden hair loss. It sucks when you notice your hair is falling out. It can happen over time and it may be months before you may discover you are missing hair. Yikes!
Let’s Talk About Hair Follicles
Hair follicles are like tiny factories within your skin that play a crucial role in both hair growth and hair loss. These miniature structures are responsible for producing the hair strands that adorn your scalp. Just like a well-oiled machine, healthy hair follicles are essential for maintaining a luscious head of hair.
When it comes to hair growth, these follicles are the powerhouses. They go through a continuous cycle of activity, rest, and shedding. During the growth phase, known as the anagen phase, hair cells within the follicle divide rapidly, creating new hair strands. These strands then extend upward through the skin and emerge as the hair you see on the surface.
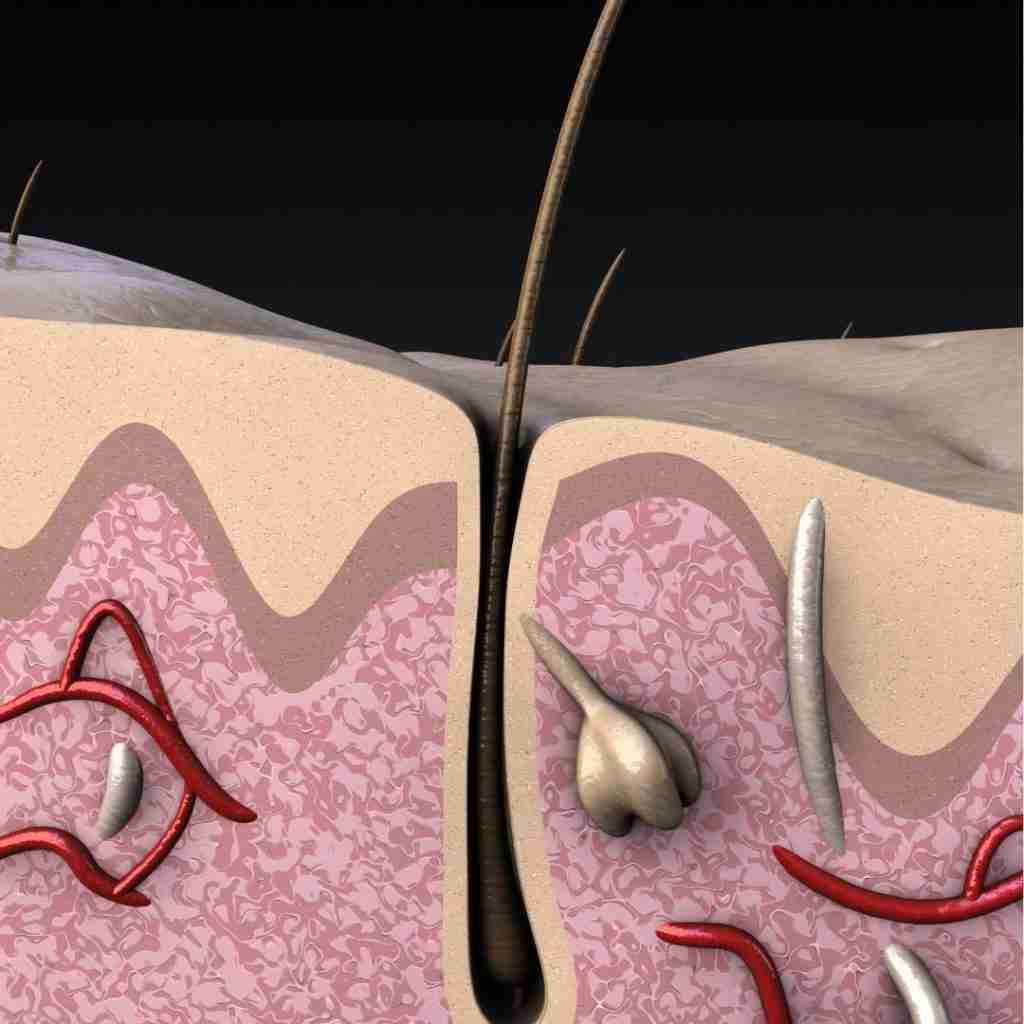
Hair Follicles and Genetics
However, not all hair follicles are created equal, and their fate is heavily influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Genetics play a significant role – the genes you inherit from your parents can dictate the sensitivity of your hair follicles to hormones like dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
When DHT binds to susceptible follicles, it triggers a chain reaction that leads to a shorter growth phase and thinner, weaker hair. Over time, this can result in hair follicles producing increasingly finer strands until they eventually stop producing hair altogether.

The Importance Of Taking Care Of Your Scalp
Understanding the critical role of hair follicles in hair loss and growth is a cornerstone of effective hair loss prevention and treatment strategies. Nourishing your scalp and follicles with proper care, a balanced diet, and appropriate hair care products can help maintain their health and prolong the growth phase of your hair.
Taking care of your scalp is just as important as pampering your face. In fact, scalp care has become one of the fastest growing beauty trends since covid hit.
Additionally, targeted treatments like minoxidil and TED treatments can stimulate blood flow to the follicles, promoting healthy growth. For those genetically predisposed to hair loss, medications like finasteride can help block the harmful effects of DHT and preserve the follicles’ function.
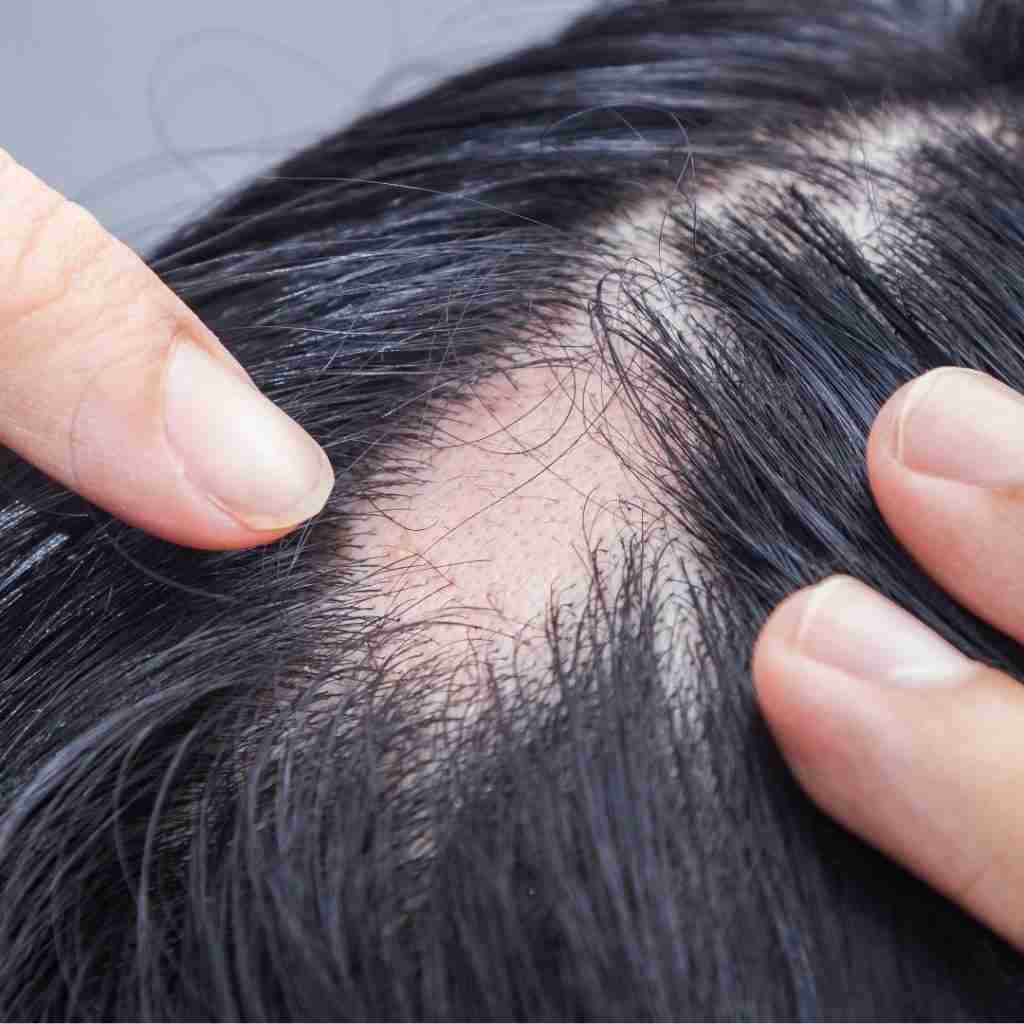
Female Pattern Hair Loss
Female pattern hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common type of hair loss in women. It typically occurs as a gradual thinning of the hair, especially in the crown and frontal areas of the scalp. While genetics play a significant role in hair growth, hormonal imbalances, aging, and underlying medical conditions can also contribute to its development.
The main symptom of FPHL is gradual thinning of hair, usually concentrated around the top of the head and the crown area. Hair shedding may increase, and the hairline usually remains intact.
Unlike male pattern baldness, which often results in a receding hairline and bald spots, female pattern hair loss tends to involve diffuse thinning across the scalp. Women may experience a wider part or see more of their scalp when their hair is pulled back.
| Society has forced women to suffer from hair loss alone due to the focus on men’s hair loss. The truth is 30 million women deal with significant hair loss! |
Common Causes Of Hair Loss In Women?
Female pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is primarily caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors.
Here are the key factors that contribute to female pattern baldness and general hair loss:
A. Genetic Predisposition
One of the primary causes of female pattern baldness is a genetic predisposition. This means that if there is a family history of hair loss, particularly on the mother’s side, the likelihood of experiencing hair loss increases. Genetic factors can influence the sensitivity of hair follicles to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which plays a crucial role in hair loss.
The most common genetic condition is known as female-pattern hair loss, or androgenic alopecia. Women with this condition might notice a widening of the part at the top of the head, often beginning when a woman is in her 40s or 50s.
B. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can trigger or worsen female pattern baldness. For example, the hormone DHT, derived from testosterone, is known to shrink hair follicles, leading to shorter and finer hair strands. Menopause may increase hair loss as well.
Some women may have increased levels of DHT or increased sensitivity of hair follicles to DHT, which can accelerate hair loss. Hormonal changes during menopause, pregnancy, childbirth, or certain medical conditions can contribute to hormonal imbalances and potentially exacerbate hair loss.
Birth control pills are also known to thin your hair for some women. On the same note, pregnant women may lose hair during the pregnancy.
C. Aging
Aging is a natural process that can contribute to female pattern baldness. As women age, their hair follicles gradually shrink and produce thinner, weaker hair strands.
This is due to a decrease in the production of certain hormones and a reduction in the blood supply to the hair follicles. Additionally, the hair growth cycle may become shorter, resulting in a decreased length of the growth phase and increased shedding.
D. Inflammation
Chronic inflammation in the scalp can damage hair follicles and lead to hair loss. Conditions such as scalp dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and autoimmune disorders like alopecia areata can cause inflammation, disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, and contribute to female pattern baldness.
E. Medical Conditions and Medications
Certain medical conditions and medications can also contribute to female pattern baldness. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and hormonal abnormalities can disrupt the balance of hormones in the body, leading to hair loss. Additionally, medications such as chemotherapy drugs, anticoagulants, and some antidepressants can have hair loss as a side effect.
F. Extreme Physical and Emotional Stress
Extreme stress can contribute to hair loss through a condition known as telogen effluvium. Telogen effluvium is a type of temporary hair shedding that occurs when there is a disruption in the hair growth cycle.
G. Hereditary Hair Loss
A strong family history of hair loss in women increases the likelihood of developing hereditary hair loss. If your mother, grandmother, or other female relatives experienced hair thinning or baldness, it may increase your risk.
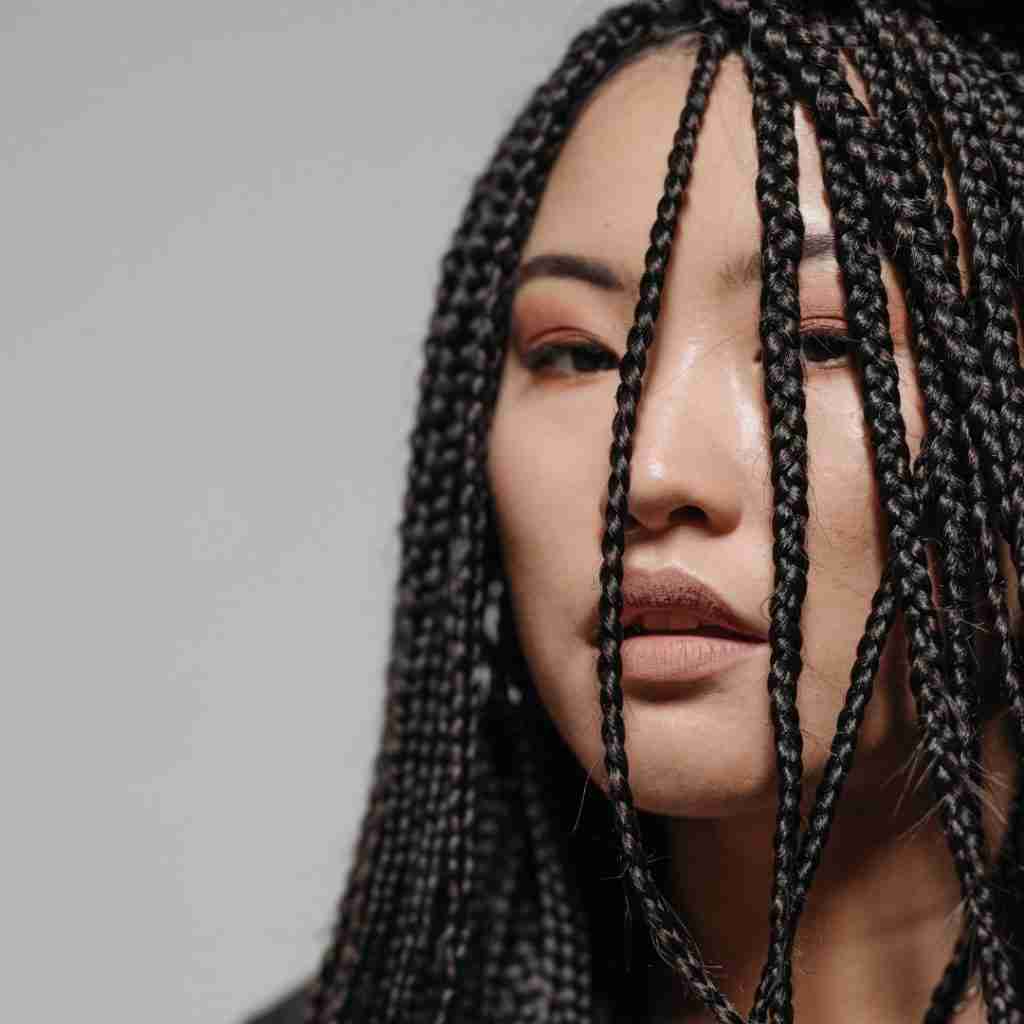

H. Hair Tension
Tight braids, particularly when worn frequently or for extended periods of time, can contribute to hair loss.
Tight braids can constrict blood flow to the scalp by pulling the hair tightly against the scalp. This reduced blood flow can compromise the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen to the hair follicles, affecting their health and leading to hair thinning or loss.
Tension on Hair Strands: The constant tension from tight braids can weaken the hair shafts, making them more prone to breakage and damage. This can result in overall hair thinning and loss over time.
I. Illness
A fever or illness can force more hairs into the shedding phase. Most people see noticeable hair shedding two to three months after having a fever or illness. Many people noticed hair falling out after covid, for example.

What Can You Do For Female Pattern Hair Loss?
The following is a list of suggestions to help restore hair loss.
1. Get your blood tested To Identify Any Issues
Blood tests can be valuable in identifying underlying factors that may contribute to hair loss in women. While specific tests can vary depending on the individual’s symptoms and medical history, here are some common areas that may be evaluated:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal imbalances can play a significant role in women’s hair loss. Blood tests can assess hormone levels, including those of estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, DHEA-S, and thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, T4). Hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders, can lead to hair loss and identifying these imbalances can help guide appropriate treatment.
- Iron Deficiency: Iron deficiency, known as anemia, is a common cause of hair loss in women. You can measure hemoglobin, ferritin, and iron levels to determine if iron deficiency is present. If iron deficiency is identified, supplementation or dietary changes may be recommended to restore iron levels and support hair growth.
- Vitamin and Mineral Levels: Deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals can contribute to hair loss. It’s important to assess levels of vitamins like vitamin D, vitamin B12, and minerals like zinc and ferritin. If deficiencies are detected, supplementation or dietary modifications can help correct the deficiencies and improve hair health.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Some autoimmune conditions, such as alopecia areata, can cause hair loss in women. Specific tests may be conducted to check for specific antibodies or markers associated with autoimmune conditions to determine if they are contributing to hair loss.
- Inflammation and infection: Inflammatory scalp conditions or infections can impact hair health and lead to hair loss. Blood tests may help identify markers of inflammation or specific infections that could be affecting the scalp.

2. Promote Hair Growth
What can you do to promote hair growth? Promoting hair growth is a key concern for women experiencing hair loss. Although there is no one-size-fits-all solution, there are several approaches that can support healthy hair growth. These include:
a. Scalp Care
Keeping the scalp clean and properly moisturized is essential for optimal hair growth. Regular shampooing, gentle massaging, and using nourishing hair products can help maintain a healthy scalp environment.
b. Hair Care Practices
Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo to cleanse your hair. Overwashing can strip your scalp of natural oils, which are important for hair health.
Regular Conditioning: Condition your hair after shampooing to keep it moisturized and manageable. Use a conditioner that suits your hair type and needs.
Avoid Heat Styling: Limit the use of heat styling tools like hair dryers, straighteners, and curling irons. Heat can damage hair fibers and lead to breakage.
Avoid Excessive Manipulation: Be gentle with your hair and avoid excessive brushing or combing, especially when it’s wet, as wet hair is more fragile.
Regular Trims: Get regular trims to prevent split ends and maintain the health of your hair. Trimming doesn’t make your hair grow faster, but it can prevent breakage and make it look healthier.
Scalp Care: Keep your scalp clean and healthy by exfoliating occasionally and massaging it to improve blood circulation. Healthy blood flow to the scalp can promote hair growth.
Use Silk or Satin Pillowcases: Sleeping on silk or satin pillowcases can reduce friction and prevent hair breakage while you sleep.
Limit Chemical Treatments: Minimize the use of harsh chemicals like perms, relaxers, and excessive hair coloring, as they can weaken the hair and lead to breakage.
Remember that hair growth is a gradual process, and results may vary. Consistency in practicing these healthy hair care habits and addressing any underlying health issues can contribute to improved hair health and growth over time.
c. Proven Hair Loss Treatments
The treatment that is proving to work for many women is Alma TED. TED is an ultrasound-based system. It uses the power of sound waves and air pressure combined with topical Hair Care Formula.
Mandy from Hair Oh Yeah in Bellevue, Washington, shares that Alma TED is a revolutionary, non-invasive hair restoration treatment.The TED device drives a specialized hair restoration solution deep into the scalp to promote blood flow, growing and fortifying the hair using sound energy and pressurized air. These benefits are achieved without the discomfort and shedding, often experienced with other hair treatment methods.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
This innovative procedure involves injecting the patient’s own platelet-rich plasma into the scalp to stimulate hair growth and improve the health of hair follicles.These procedures need to be performed by someone who is a nurse or doctor and can draw your blood. Your blood is spun in a centrifuge and the plasma is separated. This plasma (blood platelets) is then injected back into the treatment area.
Plasma can be combined with a serum. The positive is that it is your plasma and so your body readily accepts it, and it can go about healing the area. The negative is that it is your blood. IF you are older, have hormone issues or are suffering from a health condition, then you have just placed that plasma right where it might result is worsening an existing problem.
d. Topical Medications
Over-the-counter or prescription-strength topical treatments, such as minoxidil, can be effective in stimulating hair growth and slowing down hair loss in women, but it takes a long time.
e. Prescription Medications
In some cases, oral medications like finasteride may be prescribed to treat hair loss in women. These medications work by addressing hormonal imbalances that contribute to hair loss.
f. Eat A Balanced Diet
Consuming a well-rounded diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins is crucial for maintaining healthy hair growth. Foods like leafy greens, lean proteins, nuts, and seeds are excellent choices for promoting hair health.
g. Hair Transplant Surgery
In severe cases of hair loss, hair transplantation can be a viable option. This procedure involves transplanting healthy hair follicles from one area of the scalp to areas with thinning or no hair.
Hair transplant surgery may be appropriate for women who have lost their hair due to genetics, medication, pregnancy, or other circumstances. Many women experience discomfort when they lose their hair at any age. Despite trying different hairstyles, extensions, wigs, and topical creams, your results may be disappointing.
Many women experience a general thinning of their hair or a receding hairline. Those who are considering the procedure should have areas of dense hair growth where donor hair follicles can be harvested.
Thinning hair in women is a multifaceted issue that can have a significant impact on one’s self-image and confidence. Understanding the causes, types, and available treatment options is crucial for addressing this concern effectively.
By adopting a holistic approach that includes proper hair care, a balanced diet, and appropriate medical interventions, women can take proactive steps towards promoting healthy hair growth and maintaining the vitality of their hair follicles. Remember, seeking professional advice from a dermatologist or trichologist can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Most FAQ about Women’s Hair Thinning
Q. Why do women experience hair loss?
A. Hair loss in women can be caused by various factors, including hormonal changes, genetics, medical conditions (such as polycystic ovary syndrome or thyroid disorders), certain medications, and lifestyle factors.
Q. Is hair loss in women different from hair loss in men?
A. While both men and women can experience hair loss, the patterns and causes can differ. Women typically experience diffuse hair thinning throughout the scalp, while men often have receding hairlines and bald spots.
Q. What is the role of hormones in female hair loss?
A. Hormones play a significant role in hair loss among women. Changes in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy, menopause, or conditions like PCOS, can lead to hair shedding and thinning.
Q. Can styling habits cause hair loss?
A.Yes, certain styling practices like excessive heat styling, tight hairstyles, and harsh chemicals can damage the hair shaft and contribute to hair breakage and thinning.
Q. Is stress a factor in female hair loss?
Yes, stress can contribute to hair loss. Telogen effluvium is a condition where stress can push a large number of hair follicles into a resting phase, causing noticeable shedding a few months later.
Q. Can nutritional deficiencies lead to hair loss?
A. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in vitamins like Biotin, Iron, and Zinc, can impact hair health and lead to hair thinning or shedding.
Q. Are there effective treatments for female hair loss?
A. Yes, there are treatments available for female hair loss, including over-the-counter minoxidil, prescription medications like spironolactone, and low-level laser therapy. Consultation with a dermatologist or healthcare professional is recommended.
Q. Can hair loss be reversed naturally?
A. In some cases, adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and ensuring proper nutrition can help improve hair health. However, severe cases of hair loss may require medical intervention.
Q. Are there any home remedies for hair loss in women?
A. Some people find benefits from using natural remedies like scalp massages, essential oils (like rosemary or peppermint), and certain dietary changes. However, results can vary, and it’s best to consult a professional.
Learn more about the top Hair Trends- Sexy cuts and treatments here.








