Magnesium health benefits, deficiency risks and why it matters
Imagine your body as a well-rehearsed band. In this orchestra, magnesium plays the role of the master conductor, guiding every instrument and setting the tempo.
Join me on a personal journey to uncover the remarkable importance of magnesium in our bodies. Magnesium health benefits, deficiency risks and why it all matters. Believe it or not, magnesium is the unsung hero that keeps our inner symphony in perfect harmony.
My personal experience with the lack of magnesium
When I was feeling sluggish and not sleeping well, I discovered that my magnesium levels were on low side. As soon as I started taking more magnesium salt baths and supplements I was feeling like myself again.
I also noticed that when I was taking my magnesium supplements, I was more calm in general. The key is to ensure you take magnesium on a consistent basis and make it part of your everyday health routine.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.

75% of the US population are magnesium depleted
Apparently I am not alone. According to World Health Organization statistics, as much as 75% of the U.S. adult population does not meet the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s Recommended Daily Intake of 420 mg.
Long-term deficiency may cause many health issues. This includes the risk of high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes, heart disease and weak bones.
Let’s learn more about the benefits of magnesium and why we should all stay on top of our levels of magnesium.
Why Magnesium Matters- What it does for our bodies
Now, here’s why magnesium matters: It’s like a backstage superstar, helping over 300 enzymes do their thing in our bodies. These enzymes are responsible for all sorts of important jobs, like building proteins, making our bones strong, and keeping our blood sugar, blood pressure, and muscles and nerves in check.
Magnesium even plays a role in making our muscles and our hearts run well. So, it’s a pretty big deal for our overall health and well-being!

What are the main functions of magnesium in the body?
Magnesium is essential to our health and plays a major role in our everyday health. Bone health.
Magnesium is a component of bone tissue and is necessary for the development and maintenance of strong and healthy bones.
Muscle Function:
Magnesium is crucial for proper muscle function and energy production. It is involved in muscle contraction (strength training) and relaxation, which is essential for movements, including those of the skeletal muscles and the heart. Magnesium helps prevent muscle cramps and spasms.

Nerve Function:
Magnesium plays a vital role in the proper functioning of the nervous system. It is necessary for the transmission of nerve signals and helps regulate neuromuscular signals, ensuring that muscles contract and relax in response to nerve impulses.
Energy Production:
Magnesium is a key component in energy metabolism. It is required for the activation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the body’s primary energy currency. Magnesium is involved in various enzymatic reactions that are part of the cellular energy production processes.

Symptoms Of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency, also known as hypomagnesemia, can lead to a variety of symptoms and health issues. The symptoms of magnesium deficiency can vary in severity and may include:
1. Muscle Cramps and Spasms
Muscle twitching, cramps, and spasms are common early signs of magnesium deficiency. This is because magnesium is essential for muscle function and relaxation.
2. Fatigue and Weakness
A lack of magnesium can lead to feelings of weakness and chronic fatigue, as it plays a role in energy production within cells.
3. Nausea and Vomiting
Digestive symptoms like nausea and vomiting may occur with magnesium deficiency.
4. Abnormal Heart Rhythms
Low magnesium levels can contribute to irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) and palpitations.
5. Numbness and Tingling
Some people with magnesium deficiency may experience numbness, tingling, or abnormal sensations, often in the hands and feet.
6. Personality Changes
Changes in mood, such as anxiety, depression, and irritability, can be associated with magnesium deficiency.
7. Loss of Appetite
A reduced desire to eat or a lack of appetite is sometimes seen in cases of magnesium deficiency.
8. Muscle Weakness
Prolonged magnesium deficiency can lead to muscle weakness and even muscle atrophy.
9. Osteoporosis
In the long term, magnesium deficiency can contribute to a decrease in bone density, potentially leading to osteoporosis. Dietary supplements might help older women improve their bone mineral density.
10. High Blood Pressure
Low magnesium levels may contribute to high blood pressure (hypertension).
11. Tingling and Seizures
Severe magnesium deficiency can result in seizures and even hallucinations.
12. Insomnia
Magnesium is known for its potential to improve sleep quality and help with insomnia, as it can relax the muscles, calm the nervous system, and reduce stress and anxiety, which are often underlying factors in sleep disturbances.
13. Anxiety and Depression
Magnesium may help with depression and anxiety. Some research suggests that magnesium helps treat and prevent anxiety.
14. Headaches
Studies have found that magnesium supplements have helped with energy and migraine headaches. The American Migraine Foundation reports that people frequently use doses of 400–500 mg per day for migraine prevention.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can be caused by various other health conditions, so magnesium deficiency should be diagnosed by a healthcare professional through blood tests and clinical evaluation.
If you suspect a magnesium deficiency, it’s important to seek medical advice and address the issue through dietary changes, supplements, or other treatments as recommended by a healthcare provider.

Why We Need Magnesium
When you have an adequate amount of magnesium in your system, your body can function optimally, and you may experience several health benefits. Here are some of the positive effects of having enough magnesium:
Muscle Health:
Muscles function properly, and you’re less likely to experience muscle cramps and spasms.
Nervous System Function:
Your nervous system operates efficiently, which helps maintain regular nerve function, reducing the risk of tingling, numbness, and other neurological issues.
Heart Health:
Adequate magnesium levels support a regular heartbeat and help regulate blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart rhythm disturbances and high blood pressure. Too much or not enough magnesium can cause an irregular heartbeat.
Bone Health:
Your bones are better equipped to maintain their strength and density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Energy Production:
Magnesium plays a crucial role in energy metabolism, so you’ll have more energy for daily activities.
Stress Reduction:
Magnesium is associated with stress reduction and mood stabilization. It can help lower anxiety and improve overall mental well-being.
Blood Sugar Regulation:
Magnesium aids in the regulation of insulin action and glucose metabolism. It has the ability to manage blood sugar levels. This can contribute to better blood sugar control.
Immune System Support:
Adequate magnesium levels support immune system function, helping you resist infections and illnesses.
Protein Synthesis:
Proper protein synthesis ensures healthy growth, repair, and overall cellular function.
Enzyme Activation:
Magnesium serves as a cofactor for many enzymes involved in various biochemical reactions, allowing these reactions to occur efficiently.
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
Small-scale studies, including a 2012 article Trusted Source , suggest that taking magnesium supplements along with vitamin B-6 can improve PMS symptoms.
Fibromyalgia:
A preliminary clinical study of 24 people with fibromyalgia found that a proprietary tablet containing both malic acid and magnesium improved pain and tenderness associated with fibromyalgia when taken for at least 2 months.
Maintaining an appropriate balance of magnesium in the body is important for overall health and well-being. However, it’s also essential not to consume excess magnesium, as this can lead to adverse effects.
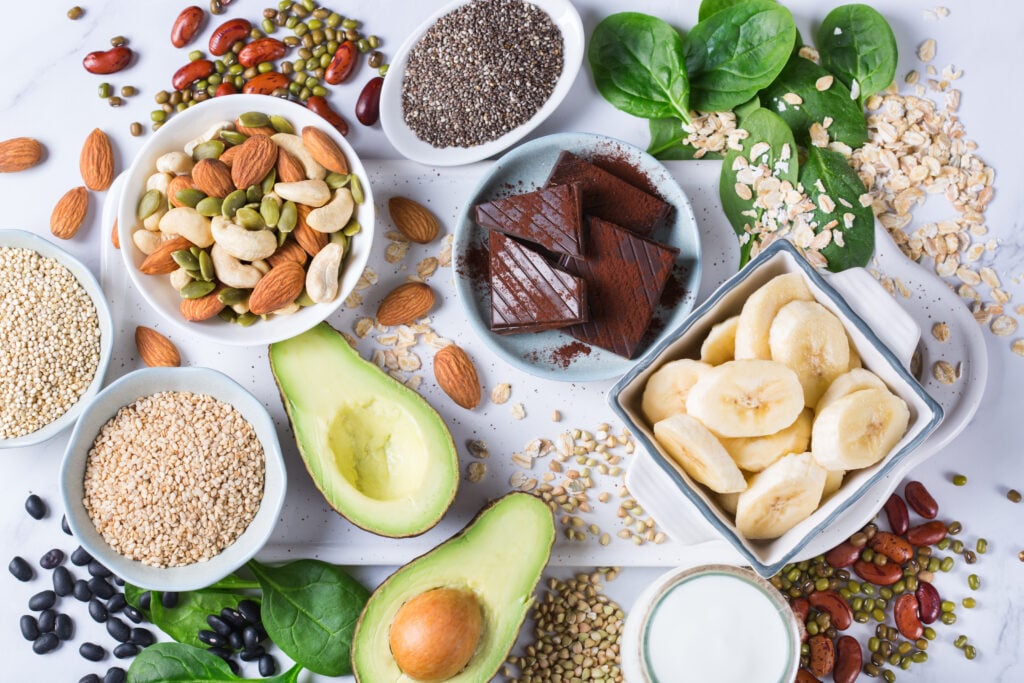

A balanced diet that includes magnesium-rich foods and supplements as recommended by a healthcare provider, if necessary, can help you achieve and maintain an optimal magnesium level in your system.
Food Sources Of Magnesium
- Nuts and Seeds:
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Pumpkin seeds
- Sunflower seeds
- Green Leafy Vegetables:
- Spinach-
- Swiss chard
- Kale
- Collard greens
- Whole Grains:
- Brown rice
- Quinoa
- Oats
- Whole wheat bread and pasta
- Legumes:
- Black beans
- Chickpeas
- Lentils
- Fish:
- Mackerel
- Salmon
- Avocado: Avocado is a fruit that’s relatively high in magnesium.
- Bananas: This fruit contains a moderate amount of magnesium.
- Dairy Products:
- Greek yogurt
- Low-fat milk
- Cheese (such as cheddar and mozzarella)
- Dark Chocolate: High-quality dark chocolate with a high cocoa content can provide a decent amount of magnesium.
- Tofu: Tofu, made from soybeans, is a good source of magnesium.
- Pumpkin: Both pumpkin flesh and seeds are rich in magnesium.
- Figs: Dried figs are a fruit high in magnesium.
It’s worth noting that the magnesium content in foods can vary depending on factors like soil quality, growing conditions, and food processing. Consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of these magnesium-rich foods can help ensure you get an adequate intake of this essential mineral.
If you have concerns about your magnesium intake, or if you have a medical condition that affects magnesium absorption, you may want to consult with a healthcare professional or consider magnesium supplements.
Types of magnesium supplements
Nearly all adult Americans lack magnesium in the diet.
Basically, we can get enough magnesium when we eat a balanced diet. However, most foods do not include enough magnesium for our daily needs. Look fortified foods–Bread and cereals with magnesium added will be labeled as fortified.
Use whole grain bread and fortified bread as it offers maximum nutrition. Similar to cereals. Choose cereal grains to avoid sugar.There are many foods are excellent sources of magnesium. Here are some of the top food sources for magnesium:
a. Magnesium Citrate:
Easy to absorb, often helps with constipation and can chill you out.
b. Magnesium Oxide:
This is a high in magnesium, but not the best at getting into your system. Good for upping your magnesium intake.
c. Magnesium Glycinate:
Super absorbable and easy on the stomach. Good for relaxing and sleep.
d. Magnesium Malate:
A buddy for those with fibromyalgia and fatigue, thanks to its connection to energy production.
e. Magnesium L-Threonate:
Known for its brain-boosting potential, as it can slip past the brain’s security.
f. Epsom Salt (Magnesium Sulfate):
Perfect for a soothing bath, eases muscle tension.
g. Magnesium Chloride:
Rub it on your skin with magnesium oil for muscle relaxation.
h. Magnesium Acetyl Taurate:
A heart and blood pressure helper.
i. Magnesium Carbonate:
This type tackles heartburn and indigestion while giving you a magnesium boost.
j. Magnesium Threonate:
Great for your noggin, as it helps your brain cells.
k. Magnesium Orotate:
Supports your heart and sports performance.
l. Magnesium Aspartate:
Boosts energy and helps your muscles.
Remember, the choice depends on your needs, so chat with a doc to pick the right one. And don’t forget about magnesium-rich foods like greens, nuts, and whole grains for a natural magnesium fix!
The table below shows the recommended daily allowance (RDA) or adequate intake (AI) of magnesium for adults, infants, and children
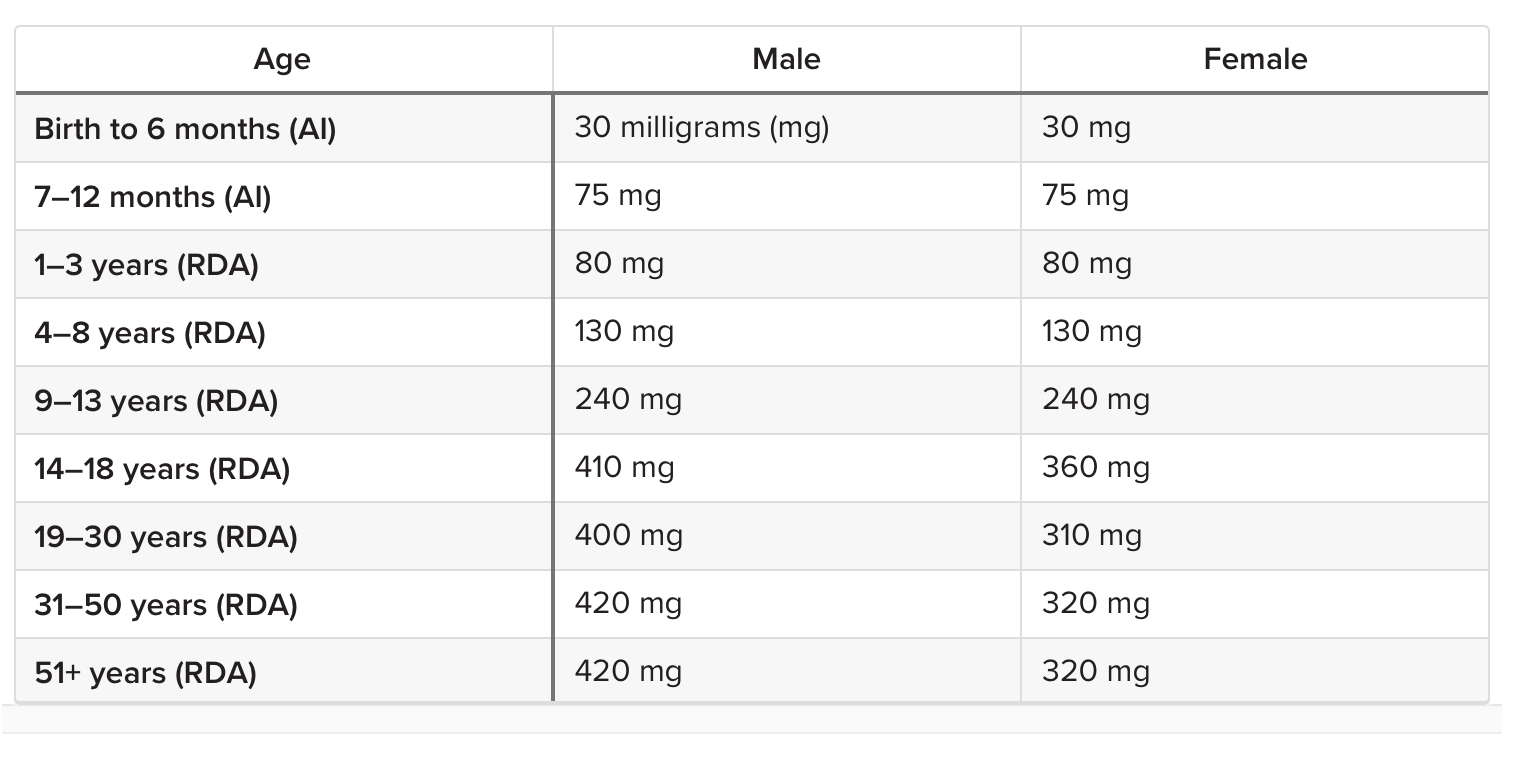
Recommended Amounts Of Magnesium
How Much Magnesium Is It Safe To Take?
Healthline says studies have found beneficial effects of magnesium when taken in doses ranging from 125–600 mg per day. However, the recommended dosage may vary depending on your needs.
Too Much Magnesium?
As with many things, more is not necessarily better. Keep in mind that too much magnesium can lead to nausea, diarrhea, vomiting and abdominal cramping.
Whenever possible, purchase supplements from brands certified by organizations like UL, USP, and NSF International.
What factors that can lower magnesium levels include:
- Drinking too much coffee, soda, or alcohol
- Eating too much sodium (salt)
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Excessive sweating
- Prolonged stress

Magnesium Bath Salt Absorption
Another way to absorb magnesium is with a simple magnesium flake bath soak. There is nothing better than easing yourself into a hot water bath (in your spa-like bathroom) after a stressful day or a long hike.
The scent of fragrant bath oils or soothing bath salts fills the air, creating a sensory oasis. The benefits of this type of soak offers much more than relaxation. It reduces anxiety and calms the body.
The chloride ions in magnesium chloride flakes are thought to enhance the absorption of magnesium. This offers significant benefits compared to Epsom salts.
Does Magnesium Interact with Medications or Supplements?
In addition, some medical conditions and medications interfere with the body’s ability to absorb magnesium or increase the amount of magnesium that the body excretes, which can also lead to magnesium deficiency.
Yes. Magnesium supplements can interact or interfere with some medicines. Here are several examples: Bisphosphonates, used to treat osteoporosis, are not well absorbed when taken too soon before or after taking dietary supplements or medications with high amounts of magnesium.
Also If you are taking a tetracycline-type medication (such as demeclocycline, doxycycline, minocycline, tetracycline), separate the time of the dose from the time of the magnesium supplement dose by at least 2 to 3 hours.