Intermittent fasting guide for endomorph & other body types
The discovery of intermittent fasting completely changed my perspective in a world filled with ever-changing diets and health crazes. It’s not just about shedding pounds; this ancient practice has an array of incredible health benefits that go beyond the superficial.
After gaining a deeper understanding of the scientific research behind intermittent fasting, I became really interested in the potential it has to rejuvenate both the mind and body. What’s even more fascinating is that practicing fasting might also extend our lifespan.
So, I decided to give it a shot. I started by avoiding food after 8 pm and simply skipping my usual early breakfast. The effects were remarkable – I felt a surge in energy and began to grasp the benefits more clearly.
Fasting Is Not A One Size-Fits-All Approach
But amidst all the buzz surrounding intermittent fasting, I realized that this journey is not a one-size-fits-all approach. We are all wonderfully unique individuals with our own biological makeup, and I couldn’t ignore the call to embrace this newfound wisdom to tailor my fasting journey according to my body type.
So, let’s embark together on this captivating adventure into the world of intermittent fasting, where science and personalization converge to unlock a path of holistic well-being.Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained popularity in recent years, and many people understand it offers various health benefits, including longevity and fat loss. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new diet or eating regimen because individual results may vary..
Here is the thing. It depends on your specific body type for the best approach to fasting. It all depends on your body type to determine the best fasting schedule and fasting methods.

Benefits Of Intermittent Fasting That May Surprise You
a. Weight Loss
Intermittent fasting may help promote weight loss by restricting the eating window, leading to a reduction in overall calorie intake. It also has the potential to enhance metabolism and trigger fat burning.
b. Improved Insulin Resistance
Improve insulin sensitivity, which is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. During fasting periods, the overall caloric intake is reduced, which can lead to weight loss or weight maintenance. Excess body weight is a significant factor contributing to insulin resistance, so losing weight through fasting can help alleviate this issue.
In addition, fasting promotes the use of stored fat as an energy source. This process, known as lipolysis, reduces the accumulation of fat in the liver and muscles, which can improve insulin sensitivity.
c. Enhanced Cellular Repair
During fasting periods, the body initiates cellular repair processes, including autophagy, where cells remove damaged components. This can aid in detoxification and overall cell health.
d. Heart Health
Some studies suggest that intermittent fasting may lead to improvements in heart health by reducing risk factors, such as cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and inflammation.
e. Brain Health
Okay, the connection between fasting and your body health looks promising so far…but what about your brain health? Some animal studies have shown intermittent fasting to be protective of the brain by improving its function and structure, like in this 2018 study in Experimental Biology and Medicine, which suggests fasting may protect against Alzheimer’s disease by reducing the incidence of memory loss.
Obviously, more research is needed to see if this is also true in humans (because you’re not a mouse, right?!)—but at some point in the future, we may see those results apply more broadly. TBD.

f. Increased Longevity
Some animal studies indicate that intermittent fasting may extend lifespan, although more research is needed to determine if this effect applies to humans. a recent study from the University of Utah’s Department of Nutrition and Integrative Physiology hints that intermittent fasting may also help you to live longer.
This study from Japan showed that not only does fasting speed up metabolism, it may also reverse the ageing process.The study on ‘what exactly happens when the body goes without food’ was conducted by researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) and Kyoto University.
They found that during fasting, 44 substances in the body increase and many of them are connected to health benefits.Previous research on the G0 Cell Unit identified various metabolites whose quantities decline with age. Leucine, isoleucine, and ophthalmic acid – have been shown to lower as a person ages.
In those who had fasted, these metabolites increased, suggesting fasting might increase molecules that help people live longer.Dr Takayuki Teruya said, “These are very important metabolites for maintenance of muscle and antioxidant activity, respectively. This result suggests the possibility of a rejuvenating effect by fasting, which was not known until now.”
g. Simplified Meal Planning
Intermittent fasting can simplify meal planning and food choices, since it often involves fewer meals per day.
h. Supports Digestive Health
Giving the digestive system regular breaks through fasting can aid in digestion and reduce issues like acid reflux and bloating.
i. Positive Impact on Hormones
Intermittent fasting can influence various hormones, including human growth hormone (HGH) and norepinephrine, which play roles in metabolism and fat burning.
j. Psychological Benefits
Some individuals report improved mental clarity, focus, and a sense of discipline and control when practicing intermittent fasting. Many people report experiencing improved mental focus and clarity during fasting periods. When the body is not focused on digesting food, it may allow the mind to feel more alert and focused.
k. Helps With Chronic Inflammation
Fasting has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body. Fasting helps with inflammation by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines, promoting autophagy, lowering oxidative stress, improving insulin sensitivity, modulating gut microbiota, and impacting adipose tissue to decrease inflammation in the body.
Remember that while intermittent fasting has potential benefits, it might not be suitable for everyone. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with a history of eating disorders, and those with certain medical conditions should avoid fasting or do so under medical supervision. It’s crucial to listen to your body and adopt a fasting pattern that suits your lifestyle and health needs.
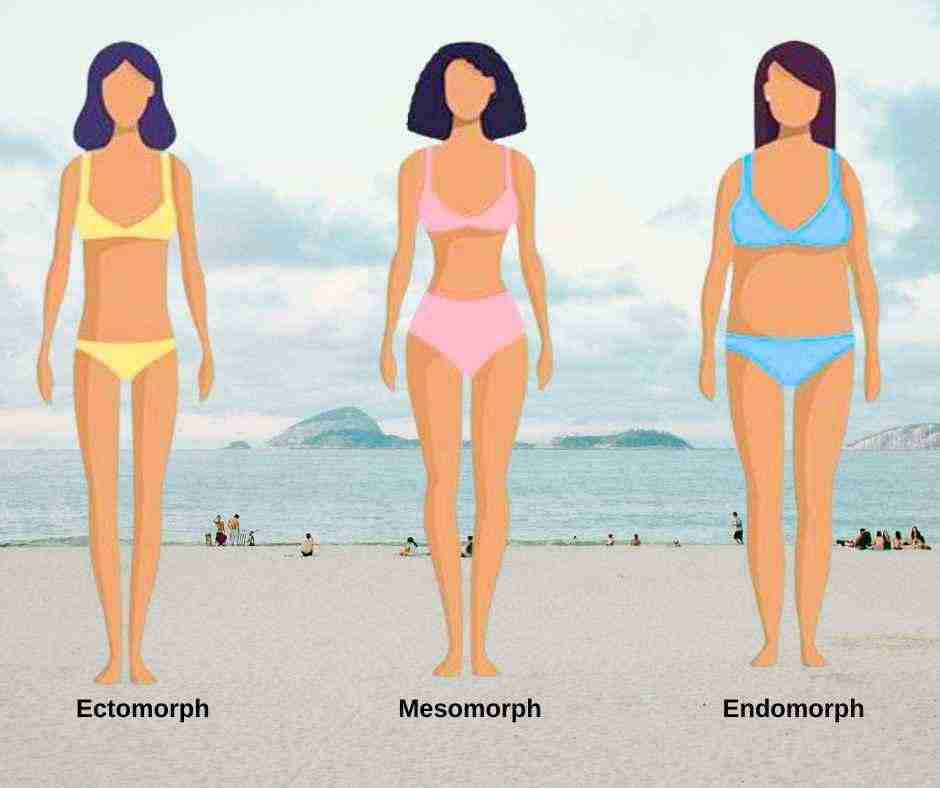
The concept of body types, including endomorphs, ectomorphs, and mesomorphs, is a classification system used to describe individual variations in body shape and metabolism. However, it’s important to note that the science behind body types is not well-supported and there is limited evidence to suggest that specific fasting strategies are inherently better for each body type.
That said, here’s a general overview of the different body types and some considerations for fasting:
Three types of body types defined by psychologist William Sheldon
According to Sheldon, there are three somatotypes: slim ectomorphs, muscular mesomorphs, and smooth endomorphs. Endomorphs, in his view, are relaxed and sociable, mesomorphs active and assertive, and ectomorphs quiet and restrained. Three somatotypes are ideal types: most people have a mixture of multiple somatotypes.
Intermittent Fasting Guide For Endomorph Body Types
1. Endomorph Body Type And Fasting
Endomorphs are often described as having a higher percentage of body fat, a rounder physique, and a tendency to gain weight more easily. They may have a slower metabolic rate compared to other body types.
Typically, endomorph body types have a wide waist and hips and large bones, though they may or may not be overweight. Their weight is often in their hips, thighs, and lower abdomen. Endomorphs often have lots of body fat and muscle and tend to gain weight easily.Endomorphs may find it challenging to maintain their fitness levels as they tend to be more susceptible to gaining weight.

2. Losing Weight With Intermittent Fasting As A Endomorph
Nevertheless, an effective approach for endomorphs to shed those extra pounds is intermittent fasting, which offers both powerful results and health advantages, such as decreased inflammation and better insulin regulation. It’s important to select a fasting window that fits your lifestyle and preferences, while also incorporating nutrient-rich foods into your meals, such as salmon, berries, spinach, oats, and chicken breast. For endomorphs, intermittent fasting is an obvious and smart choice to achieve their fitness goals.

Endomorphs face challenges in losing weight due to factors like a slower metabolism, higher fat storage, and potential insulin sensitivity. The good news is that , intermittent fasting can be particularly beneficial for endomorphs.
By incorporating intermittent fasting, endomorphs can leverage its effectiveness in weight loss, as it helps regulate insulin levels, reduce inflammation, and promote fat burning. This approach, coupled with a balanced diet (including lean protein and healthy foods) and lifestyle changes, offers a promising strategy for endomorphs to achieve their weight loss goals successfully.
Fasting Guide for Endomorphs:
Endomorphs might find it beneficial to focus on longer fasting periods (e.g., 16:8 or 18:6) to allow their body more time to tap into stored fat reserves. They should prioritize nutrient-dense foods during eating windows to support their metabolism and overall health. Managing hunger during fasting might be more challenging for endomorphs, so they may benefit from starting with shorter fasting periods and gradually increasing the fasting window.
3. Best Intermittent Fasting Types For Endomorphs
Although there are several fasting plans, endomorphs can try different fasting types and figure out what suits better for them. Depending on their body type and preferences here are some effective fasting plans.
- The 16/8 method: This method involves fasting for consecutive 16 hours and eating meals within the following 8 hours window. This can be one of the highly effective fasting plans for endomorphs as it restricts the overall calorie intake for a prolonged period of time. It also helps regulate the body’s circadian rhythm, which results in improved metabolism and fat burning.
- The 5:2 diet: In this plan, you can eat normally for five days a week and fast for two non-consecutive days. However, you can ingest up to 500 to 600 calories during the fasting days. This method is beneficial to endomorphs because they can reap the benefits without giving up normal eating.
- Alternate Day Fasting: This method is highly recommended for endomorphs because it involves fasting every other day and then eating normally the day after. During the fasting days, they can restrict their caloric intake to 500 -600 calories. According to a 2020 study, ADF is an excellent strategy for weight loss in obese individuals.

4. Ectomorph Body Type And Fasting
Ectomorphs are typically characterized by a lean and slender body with a fast metabolism. They may find it difficult to gain weight and muscle mass.An ectomorph is one of the three somatotypes, and individuals with this body type typically exhibit the following characteristics:
- Lean and Slender: Ectomorphs tend to have a slim and delicate build with narrow shoulders and hips. They often have a low percentage of body fat and a fast metabolism.
- Hard to Gain Weight: Ectomorphs often find it challenging to gain both muscle and fat, even when consuming a high-calorie diet. This is due to their naturally high metabolic rate and fast calorie burning.
- Long Limbs: Ectomorphs typically have long, lean limbs, which can give them an elongated appearance.
- Narrow Frame: Their bone structure is usually narrow, and joints are often small.
- Limited Muscle Mass: Gaining muscle can be more difficult for ectomorphs compared to the other body types. They may have a more “linear” or less muscular appearance.
Fasting Considerations: Ectomorphs might need to be cautious with very long fasting periods, as they may have higher calorie needs and could risk losing muscle mass. They could consider shorter fasting periods (e.g., 14:10) or time-restricted eating to ensure they meet their nutritional requirements. Ensuring sufficient calorie intake and including strength training in their routine can help maintain muscle mass.

4. Common Mesomorph Body Type And Fasting
Mesomorphs are often seen as having a more athletic and muscular build. They tend to have a balanced metabolism and find it easier to gain and lose weight.
Mesomorph Body Type Characteristics:
- Muscular and Athletic Build: Mesomorphs tend to have a naturally muscular and athletic physique. They have well-defined muscles and a higher percentage of muscle mass compared to the other body types.
- Broad Shoulders and Narrow Waist: Mesomorphs often have broad shoulders and a narrower waist, creating a V-shaped or hourglass-like body silhouette.
- Responsive to Exercise: Mesomorphs tend to respond well to strength training and physical activity, making it relatively easier for them to build muscle and improve their overall fitness levels.
- Efficient Metabolism: They usually have a moderately fast metabolism, which can help them maintain a healthy body weight without much effort.
- Easily Gains and Loses Weight: While mesomorphs may gain muscle and lose fat relatively easily, they can also gain weight if they do not engage in regular physical activity and maintain a balanced diet.
- Medium Bone Structure: Mesomorphs typically have a medium-sized bone structure, which contributes to their well-proportioned appearance.

It’s important to note that very few individuals fit perfectly into one specific body type category. Most people display a combination of characteristics from multiple somatotypes. Additionally, while Sheldon’s somatotype theory was popular in the past, contemporary research suggests that genetics, lifestyle, and other factors have a more significant impact on body composition.
Understanding your body type, including whether you lean more towards a mesomorph, ectomorph, or endomorph, can provide insights into how your body responds to different training and nutrition approaches. However, it’s crucial to remember that individuality plays a significant role, and tailored fitness and nutrition plans are essential to meet specific goals and achieve overall well-being.
An ectomorph is one of the three somatotypes, and individuals with this body type typically exhibit the following characteristics:
Fasting Considerations: Mesomorphs may have more flexibility in choosing a fasting strategy. They could try various approaches, such as 16:8, alternate-day fasting, or 5:2 fasting, and see what suits them best. Balancing their fasting routine with a well-rounded diet and regular exercise can support their fitness and health goals.

What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is a popular eating pattern that involves cycling between periods of fasting and eating. The most common method is the 16/8 method, where individuals fast for 16 hours and consume all their meals within an 8-hour window, often skipping breakfast and eating between noon and 8 p.m.
Other types of intermittent fasting diet include the 5:2 diet, where individuals eat normally for five days a week and eat fewer calories (eat on alternate day-500-600 calories) . A good option is the eat-stop-eat method, where individuals fast for 24 hours once or twice a week, for example, from dinner on Monday to dinner on Tuesday.
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity for various reasons, including potential weight loss benefits, improved insulin sensitivity, cellular repair, and other positive effects on health.
However, it’s essential to approach intermittent fasting with caution and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian, especially if you have any medical conditions or concerns. The effectiveness and suitability of intermittent fasting can vary among individuals, and it’s crucial to find an approach that fits your lifestyle and health goals.
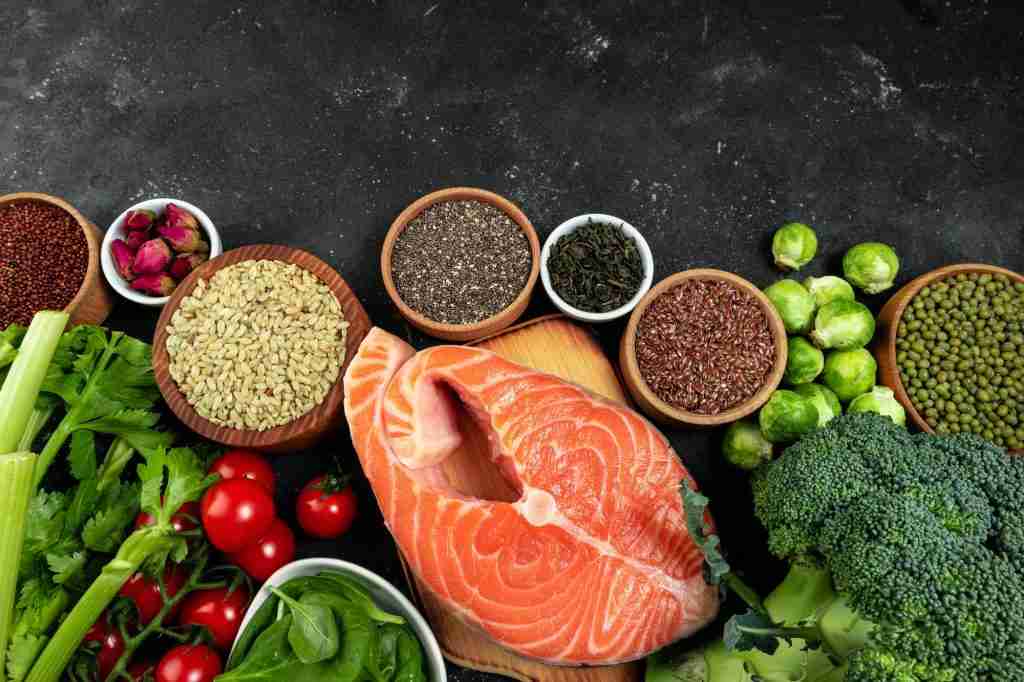

What To Eat When You Are Intermittent Fasting:
During intermittent fasting, the focus is not on what you eat but rather on when you eat. The primary goal is to cycle between periods of eating and fasting. However, what you eat during your eating windows can still significantly impact your overall health and well-being. There are 6 metabolism busting foods to avoid- read more here.
Here are some tips on what to eat while intermittent fasting:
- Whole Foods: Opt for nutrient-dense whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, nuts, and seeds. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber to support your overall health.
- Proteins: Incorporate lean protein sources like chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, legumes, and lentils. Protein can help you feel full and satisfied during fasting periods.
- Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds. Healthy fats can provide sustained energy and aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Choose complex carbohydrates like sweet potatoes, quinoa, brown rice, and whole-grain bread. They provide more sustained energy and are less likely to cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Plenty of Water: Stay well-hydrated during both fasting and eating periods. Water can help control hunger and ensure proper body function.
- Avoid Sugary and Processed Foods: Minimize or eliminate foods high in added sugars and processed ingredients. These can lead to energy crashes and negatively impact your health.
- Be Mindful of Portions: Pay attention to portion sizes and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues to avoid overeating.
- Stay Balanced: Aim for a balanced diet that includes a variety of food groups to meet your nutritional needs.
Remember, intermittent fasting can be personalized based on your lifestyle and preferences. Some people may find success with specific diets like the Mediterranean diet, the ketogenic diet, or plant-based diets while practicing intermittent fasting. It’s essential to find what works best for you and consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian if you have any specific health concerns or dietary restrictions.
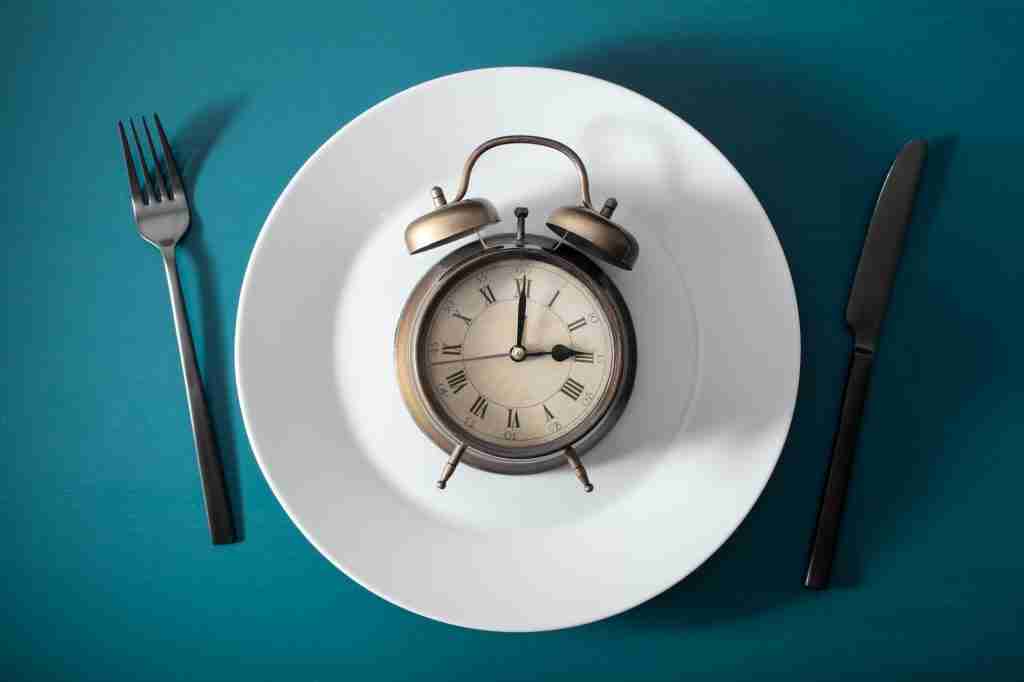

For the best results with intermittent fasting, consider the following tips:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water during fasting periods to stay hydrated and help control hunger.
- Nutrient-Dense Meals: Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods during your eating window to provide your body with essential nutrients.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body’s signals and adjust your fasting schedule or approach if you feel overly fatigued or unwell.
- Exercise: Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, as it complements the benefits of intermittent fasting.
- Be Consistent: Stick to your chosen intermittent fasting method consistently to see long-term results.
- Consult a professional: If you have any health concerns or medical conditions, consult a healthcare professional before starting intermittent fasting.
Remember, intermittent fasting is not suitable for everyone, and individual responses can vary. The best approach is one that fits your lifestyle, preferences, and overall health while promoting a sustainable and balanced eating pattern.







